Understanding Cloud Computing: Empowering the Digital Revolution
Comparing Local Servers, Data Centers, and Cloud Computing: Making the Right Infrastructure Choice
When it comes to hosting and managing data and applications, businesses have various options available to them. Local servers, data centers, and cloud computing each offer unique advantages and considerations. In this blog, we will compare these infrastructure choices, exploring their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks to help you make an informed decision for your organization.
Local Servers (On-Premise Servers): Local servers, also known as on-premise servers, refer to physical servers that are housed within an organization's premises. These servers are managed, maintained, and operated by the organization's own IT team. Here are some key aspects of local servers:
Control and Security: With local servers, organizations have full control over their infrastructure and data, making it suitable for industries with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Customization: On-premise servers offer the flexibility to tailor hardware and software configurations according to specific needs.
Upfront Costs: Local servers typically require significant upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and upgrades add to the operational costs.
Data Centers (Rent Server): Data centers are dedicated facilities that house multiple servers, networking equipment, and storage resources. Organizations can rent server space and infrastructure within these data centers. Let's explore the key aspects of data centers:
Scalability and Reliability: Data centers provide scalability options, allowing organizations to scale up or down their server resources as needed. They also offer high levels of reliability with redundant power supply, backup systems, and network connectivity.
Reduced Maintenance: By renting server space in a data center, organizations can offload the responsibility of hardware maintenance and infrastructure management to the data center provider.
Connectivity and Bandwidth: Data centers offer high-speed internet connectivity, ensuring robust and efficient data transfer and network performance.
Cloud Computing : Cloud computing involves the delivery of computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, and applications, over the internet. Here are the key aspects of cloud computing:
Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud computing provides on-demand scalability, allowing organizations to quickly and easily scale their resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility makes it suitable for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront hardware investments and reduces ongoing maintenance costs. Organizations pay for the resources they consume on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud computing enables users to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and collaboration among teams.
Managed Services: Cloud service providers handle server maintenance, security, and software updates, freeing up organizations' IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Choosing the right infrastructure option for your organization depends on several factors such as security requirements, scalability needs, budget considerations, and desired control over data and resources. Local servers offer maximum control but require significant upfront investments. Data centers provide scalability and reduced maintenance but come with ongoing costs. Cloud computing offers flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and managed services, making it an attractive option for many businesses. Assess your organization's needs and evaluate the pros and cons of each infrastructure choice to make an informed decision that aligns with your goals and resources.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing resources over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, cloud computing enables users to access a network of remote servers, databases, storage, and applications for various computing needs. It eliminates the need for physical infrastructure and allows for seamless access and collaboration from anywhere, at any time.
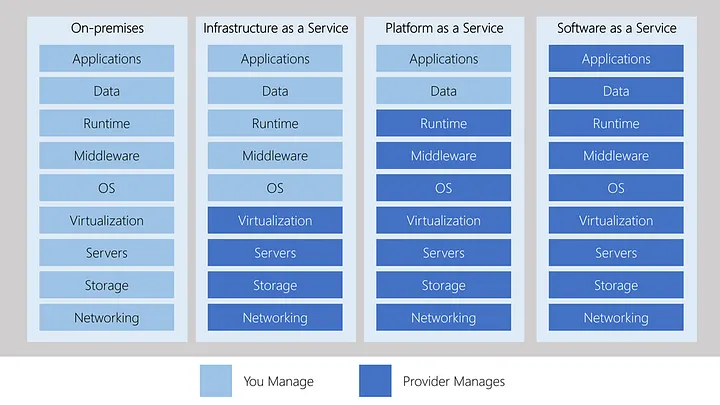
Cloud Service Models: IAAS, PAAS, SAAS
IAAS vs PAAS vs SAAS

Cloud computing offers three primary service models, each catering to different user requirements:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS): IAAS provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networks over the internet. It offers users the highest level of control and flexibility, as they can manage and control the underlying infrastructure while outsourcing the maintenance and management of hardware to the cloud provider. Examples of IAAS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Platform as a Service (PAAS): PAAS provides a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, including infrastructure, runtime, and middleware components. Users can focus on building and deploying applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. PAAS offerings include tools for application development, testing, deployment, and scaling. Popular PAAS providers include Heroku, Microsoft Azure PAAS, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SAAS): SAAS delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access them through a web browser or a client interface. With SAAS, users do not need to worry about installation, maintenance, or updates, as the software is centrally managed by the provider. Popular SAAS applications include customer relationship management (CRM) tools like Salesforce, productivity suites like Microsoft 365, and collaboration tools like Slack.
Summary :
Deployment Clouds: Public, Private, Hybrid
Cloud computing deployments can be categorized into three main types:
Public Cloud: Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party service providers who make computing resources available to the general public over the internet. These resources are shared among multiple users and organizations, offering scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are prominent public cloud providers.
Private Cloud: Private clouds are dedicated infrastructure owned and operated by a single organization. They offer increased control, security, and customization options, making them suitable for businesses with strict data privacy or regulatory requirements. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Examples include VMware, OpenStack, and Microsoft Azure Stack.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid clouds combine the best of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments. It involves integrating on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, providing flexibility, scalability, and data portability. Hybrid clouds enable businesses to keep sensitive data on-premises while utilizing public cloud resources for less critical workloads. Major cloud providers offer hybrid cloud solutions, including AWS Outposts, Azure Arc, and Google Anthos.
Cloud Providers:
Several cloud service providers offer a wide range of services and solutions to meet diverse business needs. Some of the leading cloud providers include:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform
IBM Cloud
Oracle Cloud
Alibaba Cloud
Conclusion: Cloud computing has become an indispensable technology that fuels the digital transformation of businesses and empowers individuals worldwide. With its service models, deployment options, and a vast array of cloud providers, organizations can choose the most suitable cloud solutions to enhance efficiency, scalability, and innovation. By embracing cloud computing, businesses can unlock the full potential of the digital revolution and stay ahead in the competitive landscape.